how digital payments help reshape the world economies

Digitizing payments is not the implementation of internet and mobile banking solutions, it’s a confrontation between financial digital transformation and traditional paradigm governing banking institutions. Payments is an area which we focus on deeply, as it provides enough dynamism to monitor the disruption that digital financial tools can cause on the banking model for a decade and beyond.
A combination of digital innovations, coupled with an incessant desire from financial leaders to drive the digitization of financial institutions, is setting the pace towards a new digital economy. In this paper we discuss the ongoing narratives were digital payments implied positive economic consequences on a macro and micro economic level.
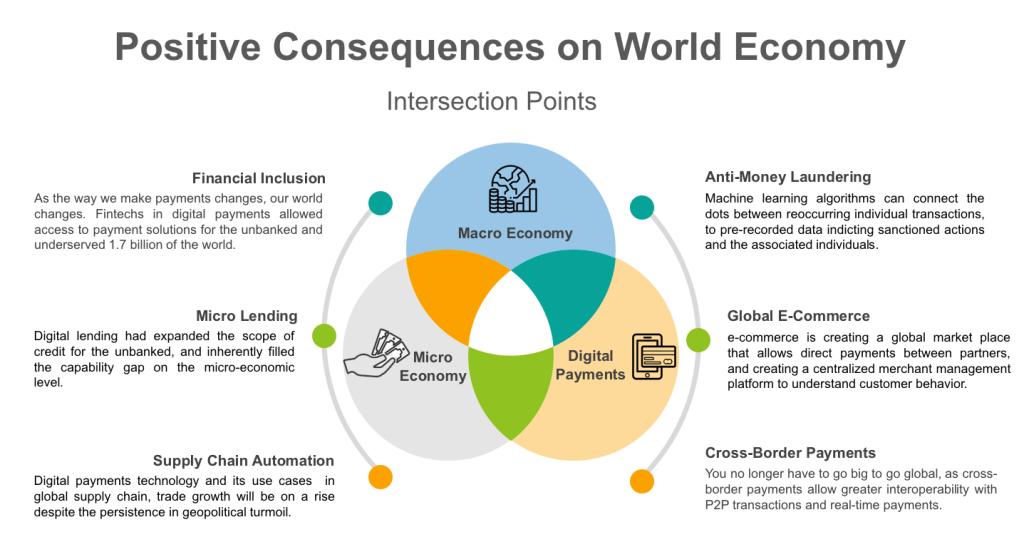
Financial Inclusion
Digital payments are inherently providing financial inclusion; through their scalable nature, fintechs in the payments field can deliver financial services to a wider set of audience, and expand payments services to the non-financial sector; in the MENA alone, 22% of the population had adopted fintech in 2020. The significant increase in mobile technology acquisition and its usage across the MENA, where 45% of the population has access to mobile technology, had enabled the scalability and fast deployment of fintech payment solutions to the end consumer.
Anti-Money Laundering
In terms of AML initiatives, governments heavily rely on the banking sector to monitor, access, and report on money laundering activities. The current approach and adopted technologies are short-sighted in terms of monitoring and processing the entire picture of money laundering connections. A re-visitation of AML frameworks is out to be recognized by central banks, from the early stages of evaluating KYCs to proposing new investigative measures, machine learning fintech solutions are key to enable a well-rounded approach to money laundering investigations. Machine learning algorithms can connect the dots between reoccurring individual transactions, to pre-recorded data indicting sanctioned actions and the associated individuals or organizations.
The joint effort of fraud investigators in identifying peer-to-peer digital payment, and machine learning algorithms, can fullfil a more detailed module to catch the tip of the iceberg on any money laundering activity involving digital payments or transactions.
Cross-border Payments on Global Supply Chain
To adhere to the effects of digital payments on supply chain automation, we are considering the very specific case of using block chain technology; based on DLT, block chain payments record all sets of data involved in a transaction in real-time, from pre-transaction stage to post-transaction monitoring, companies or governments involved in cross-border trade can revolutionize how they conduct payments and reply to various supply and demand patterns. Block chain technology in cross-border payments can set supply chain immune to any fraudulent payments or data breaching attempts. Block chain payments also allow to trace back trade’s origin, time of purchase, and travelled-to destinations, as well as keep an accurate measure of the accuracy and efficient of the supply/demand process. Given the outlooks on digital payments technology and its use cases opportunities in global supply chain, trade growth and cross-border payments will be on a rise despite the persistence in geopolitical turmoil, as the process of cross-border peer-to-peer transactions become facilitated by block chain payments.
Merchant Innovation & Global e-commerce
On the Micro end of the economic spectrum, payment innovations had been transforming how SMEs operate their business. Nowadays customer satisfaction is the new gold, and e-commerce in the pandemic era was able to gauge the needs of consumers and their business, and the code was digital payments. MasterCard reports a record surge in digital payments growth rates across the globe, as consumers increasingly shop online. Global e-commerce is on the rise, and creating especially a trend in the B2B and C2B markets, as digital payments were used for small item purchases, and due to their increasing comfort in transaction speed and heightened security. We might view e-commerce transactions as a trend, but e-commerce is creating a global market place that can payments across global partners, allowing P2P mobile wallet payments amongst for B2B and C2B institutions, while also creating a centralized merchant management platform to further understand and record customer behavior.
Digital Micro-Lending and SMEs Growth
The amount of micro lending had seen a frantic activity in the emerging economies of the world; with proliferation of data and wide availability of mobile technology, the micro lending space was led by fintechs, allowing the non-financial sector access to short term loans, and exponential innovation in digital lending allows SMEs to pass-on their loans to their customers using closed-loop payment networks. The smart android POS technology had changed the front-end of the consumer micro-lending experience, where applying to a loan, or the on-boarding experience is more intuitive, seamless and convenient; powered by algorithmic and machine learning technology, the smart POS can make a decision in a few minutes. Digital lending had expanded the scope of credit for the unbanked, and those previously underserved, and inherently filled the capability gap on a micro-economic level.